Everything You Need to Know About the Flu
Flu, also known as influenza, is caused by influenza viruses that infect the respiratory tract – this includes your nose, throat, and lungs. It is highly contagious and is spread by breathing in droplets from the coughs and sneezes of an infected person.1
Flu affects people of all ages and can sometimes cause serious illness, even in healthy people. It is a seasonal infection that most commonly circulates during the winter months.1,2 Flu varies from year to year – sometimes flu season can cause mild infection and be short in duration. Other times, there may be a longer flu season that causes more severe illness than previous years.1
Early signs of the flu
You may notice some early signs of the flu that indicate you’re becoming ill. Early signs of the flu can include:6
- A sudden cough
- Headache
- A sudden fever
- Aches or pains
- Sore throat
- Intense fatigue
Types of Flu
Influenza viruses can be divided into three main types – A, B and C. Influenza type A and B are the most common causes of flu, and cause most of the flu outbreaks and epidemics (defined as the widespread occurrence of an infectious disease within a community at a particular time). Influenza type C typically causes sporadic, mild respiratory symptoms and can cause an illness in children that resembles the common cold.4,10
Most people infected with the flu have influenza type A. This type of influenza virus has caused most of the worldwide epidemics.10 Influenza type A can also infect animals, and sometimes this infection can be passed from animals to humans. 10 Subtypes of influenza type A include:
- Avian influenza (H5N1): Also known as ‘bird flu’ since it mainly affects birds. This virus can cause serious infection and death in humans, but the number of human cases has been low, and it hasn’t been found in Australia. It can spread from infected birds to humans, but there’s no evidence that it passes from person-to-person.10
- Swine flu (H1N1): Found in pigs but can spread to humans. Infection is mild for most people but can cause serious infection in high-risk groups, such as those with chronic conditions, pregnant people and Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander people. H1N1 caused a global pandemic in 2009, which ended in August 2010.10
When to See a Doctor for the Flu
If you have flu symptoms but you’re otherwise fit and healthy, there’s no need to see a doctor. However, you should see a doctor if you or your child has flu symptoms and:12
- are younger than 5 years old
- are aged 65 years or older and living in an aged care home
- are pregnant
- are very obese
- are an Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander person
- have severe asthma, breathing problems or a lung disease
- have a disease that affects your muscles and/or the nerves that control them, and that can affect your ability to breathe
- have a weakened immune system
- are homeless
- are a smoker
These conditions may mean that you’re more likely to get seriously ill with the flu, so see your doctor if you have any of the above conditions and flu symptoms.12
Additionally, you should see a doctor if you or your child have flu symptoms and: 12
- can’t or won’t drink fluids
- are vomiting frequently and/or are unable to drink fluids
- have an intense headache
- are pale and feel sleepy
- have chest pain
- are experiencing breathing difficulties
- develop a rash with fever
- are experiencing neck stiffness
- find light hurts their eyes
- are worried
Lemsip Products
Lemsip has a range of over-the-counter cold and flu relief products, designed specifically for the symptoms you are experiencing:
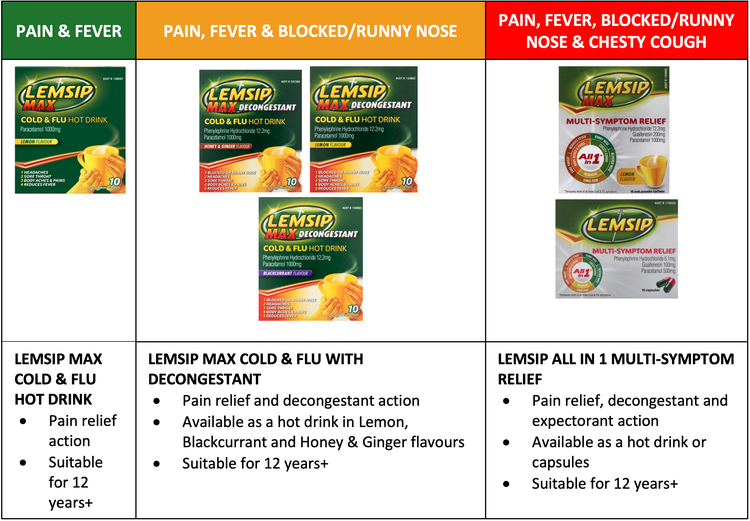
You can pick Lemsip products up from your local pharmacy or supermarket. They have different active ingredients and different formulations. If you are unsure which formulation is right for you, talk to your pharmacist.
[Disclaimer]
This article is for general information only and not intended as a substitute for medical advice. All information presented on these web pages is not meant to diagnose or prescribe. In all health-related matters, always consult your healthcare professional.
[AU Mandatories]
Always read the label and follow the directions for use. Incorrect use could be harmful. RKT-M-01558.
References
1. Better Health Channel. Flu (influenza). Updated March 2018. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/. Accessed August 2020.
2. Health Navigator New Zealand. Influenza vaccine for adults. Updated September 2022. https://www.healthnavigator.org.nz/medicines/i/influenza-vaccine-adults/. Accessed October 25, 2022.
3. Eccles R. 2009 Mechanisms of symptoms of common cold and flu. In: Eccles R., Weber O. (eds) Common Cold. Birkhäuser Advances in Infectious Diseases (BAID). Birkhäuser Basel
4. Moghadami M. A narrative review of influenza: A seasonal and pandemic disease. Iran J Med Sci 2017;42(1):2–13
5. Uyeki TM. In the Clinic: Influenza. Ann Intern Med 2017;167(5):ITC33-ITC48.
6. Queensland Health. What’s the difference between a cold and the flu? Available at: https://www.health.qld.gov.au/newsroom (accessed July 2020).
7. Greatorex JS, et al. Survival of influenza A(H1N1) on materials found in households: Implications for infection control. PLoS One 2011;6(11):e27932
8. Barker J, et al. Spread and prevention of some common viral infections in community facilities and domestic homes. J Appl Microbiol 2001;91(1):7-21.
9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. How Flu Spreads. Updated August 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/about/disease/spread.htm
10. HealthDirect. Influenza A. Available at: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/influenza-a-flu. Accessed September 08, 2022.
11. Jacobs SE, et al. Human rhinoviruses. Clin Microbiol Rev 2013;26(1):135-62.
12. HealthDirect. Influenza . Available at: https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/flu. Accessed September 08, 2022.
13. Singh B, et al. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1909.
14. HealthDirect. Vitamin A and your health. Reviewed September 2022. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/vitamin-a-and-your-health. Accessed September 07, 2022.
15. HealthDirect. Vitamin C and your health. Reviewed September 2022. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/vitamin-c-and-your-health. Accessed September 07, 2022.
16. HealthDirect. Vitamin D and your health. Reviewed September 2022. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/vitamin-d-and-your-health. Accessed September 07, 2022.
17. Better Health Channel. Flu (influenza) – immunisation. Updated April 2019. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/flu-influenza-immunisation. Accessed August 2020.


